AI-Powered XPath Generation (Web)
The Optimized XPath Generation feature automatically creates stable, unique, and minimal XPath expressions for web elements. This ensures faster, more reliable, and maintainable test automation across web applications, improving script robustness, reducing manual effort, and enhancing overall test execution efficiency.
Step 1: Default Locator Behavior During Execution
a) When a user runs a test execution, the ‘Relative XPath’ automatically appears as the default locator at the step of details, and ‘Automator XPath’ comes as a secondary path.
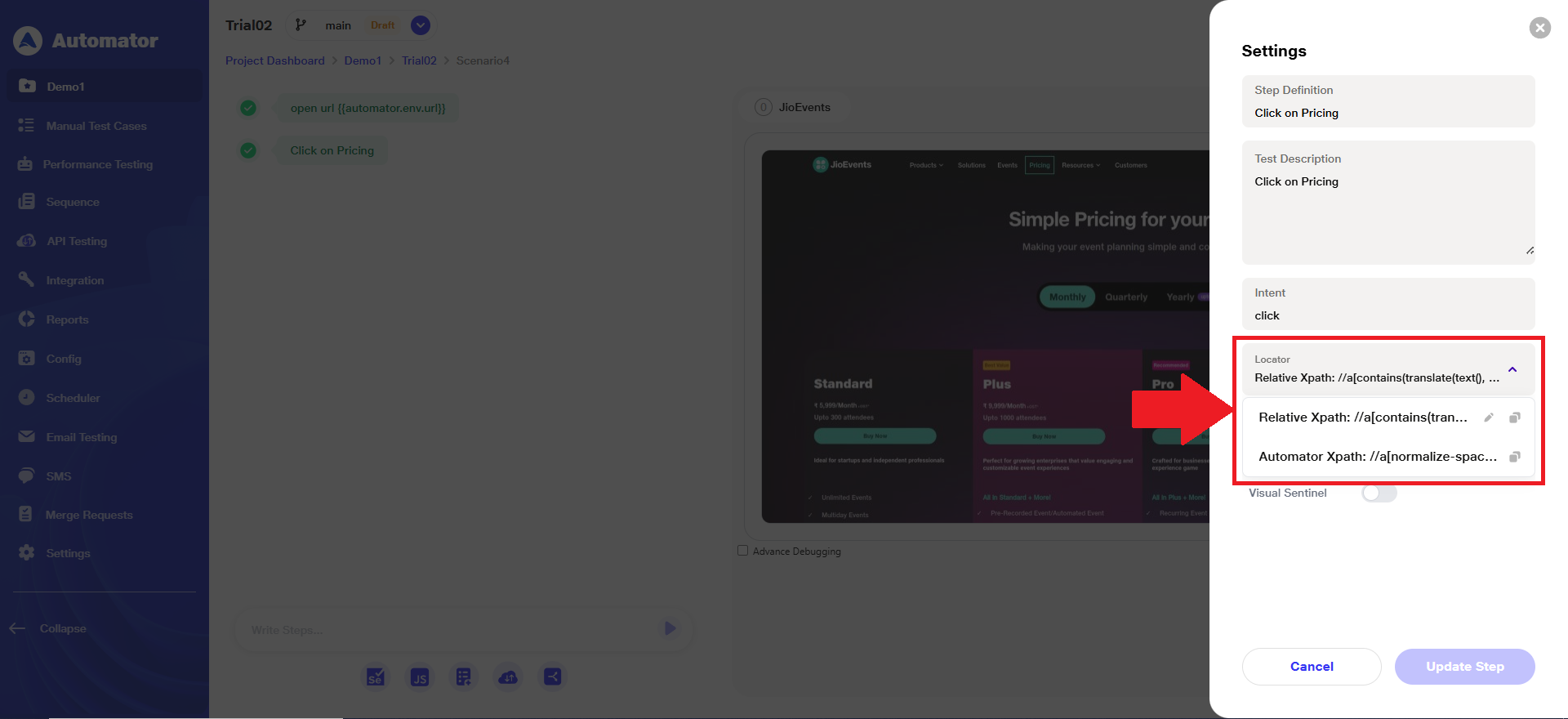 Please Note: The Relative XPath’ is editable, and the ‘Automator XPath’ is system-generated and non-editable.
Please Note: The Relative XPath’ is editable, and the ‘Automator XPath’ is system-generated and non-editable.
b) If any step fails during execution, and user performs ‘Quick Heal’, then the ‘Automator XPath’ will remain as the default locator, and four additional Chrome locators will appear in the list for reference and fallback.
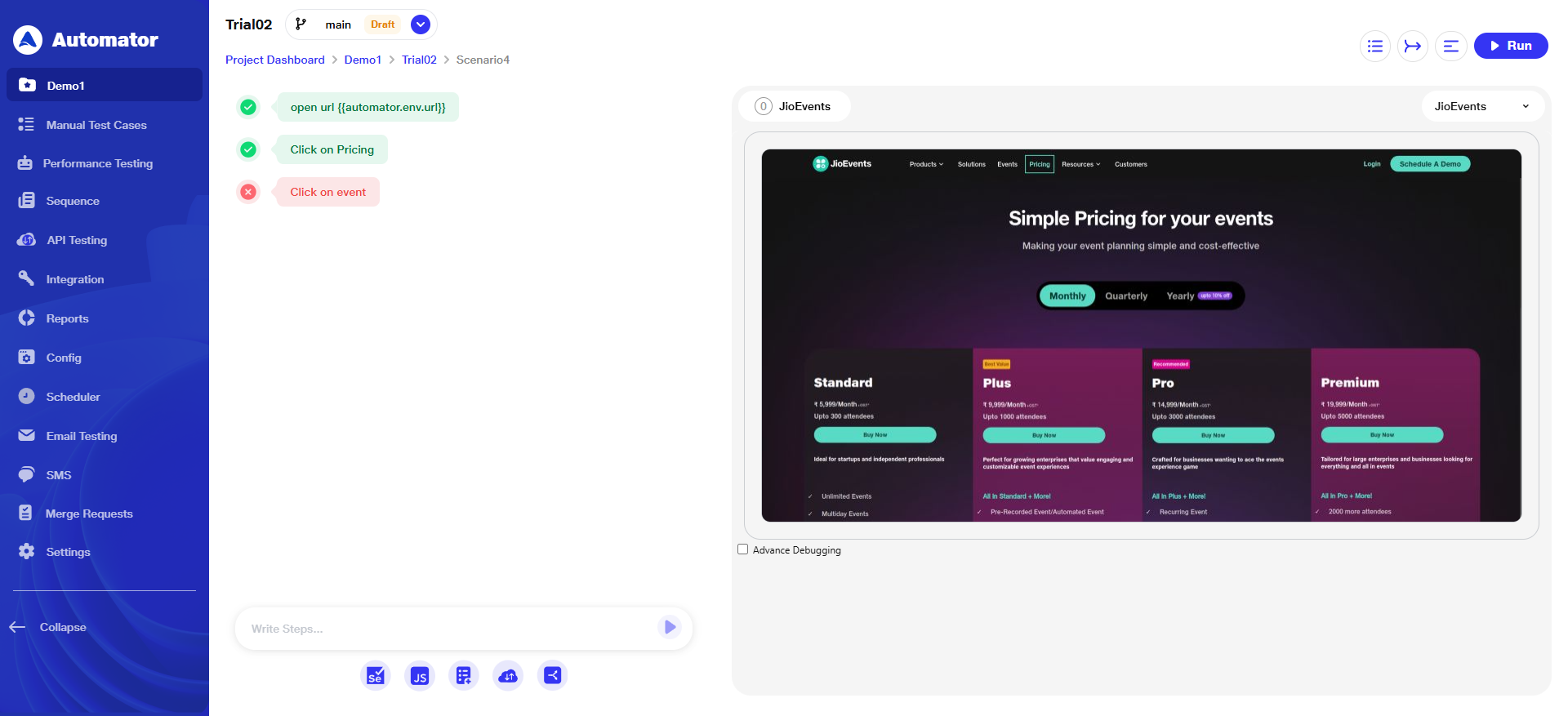
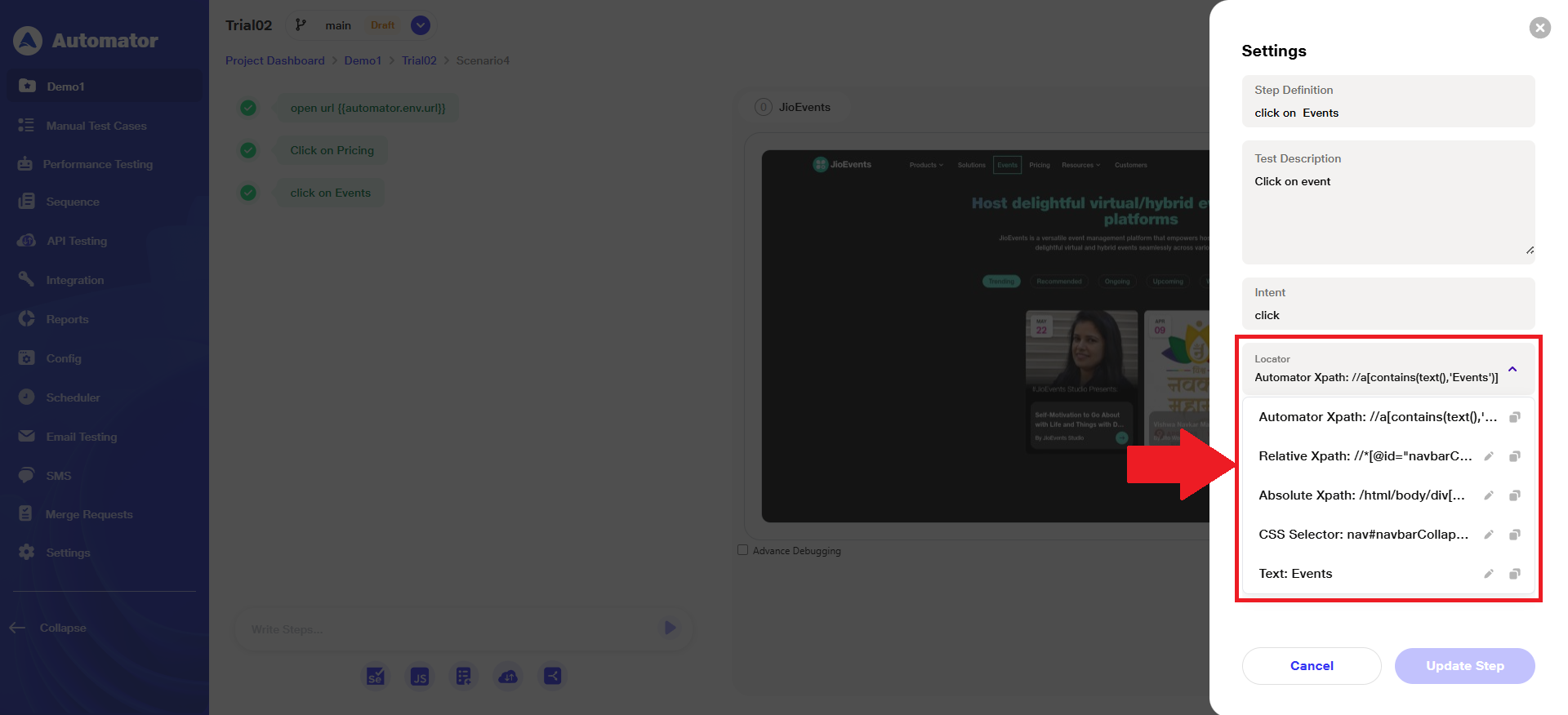 Please Note: Other four additional Chrome locators are system-generated and editable.
Please Note: Other four additional Chrome locators are system-generated and editable.
Step 2: Manual Step Behavior
a) When a user writes a manual step and execution is OFF, the generic Relative XPath will appear as the default locator.
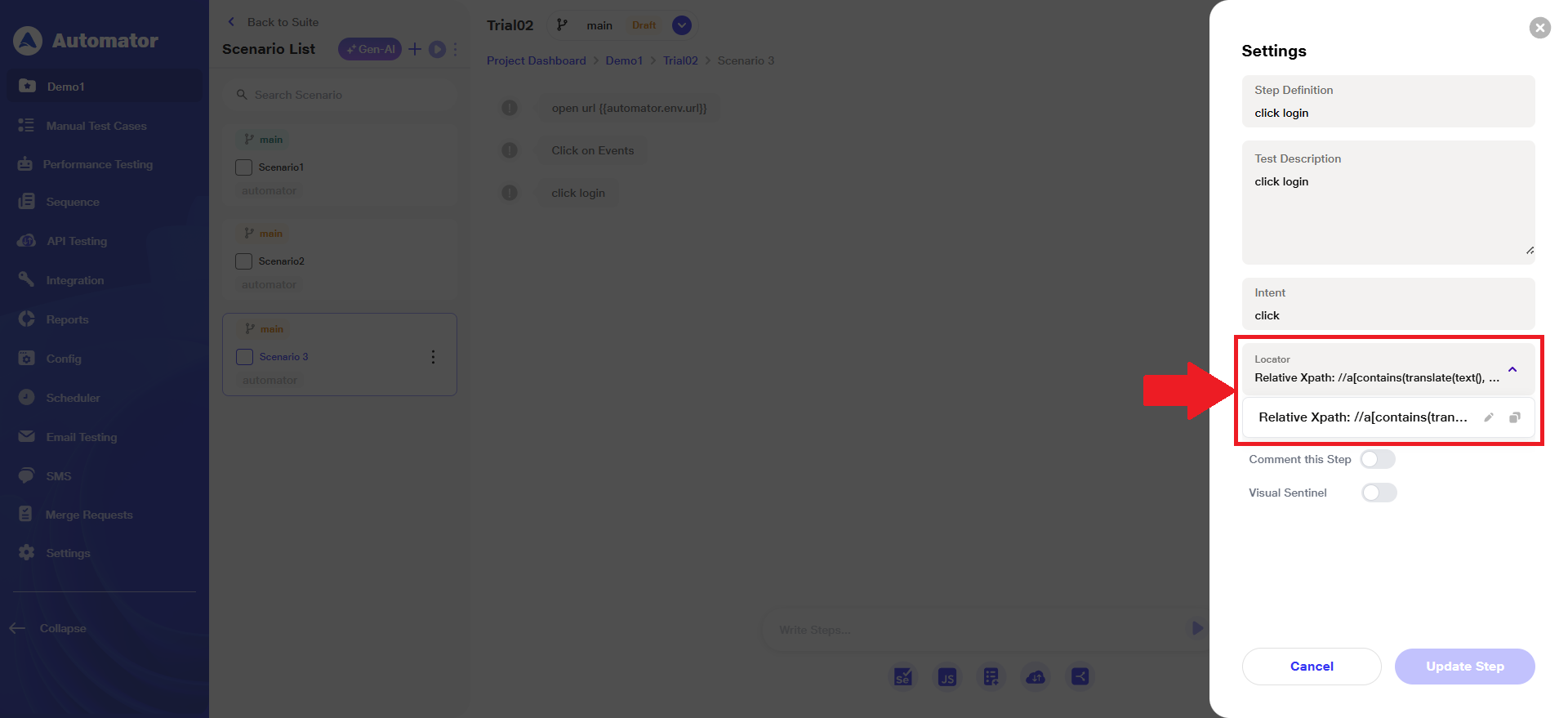 Please Note: The ‘Relative XPath’ is editable.
Please Note: The ‘Relative XPath’ is editable.
b) When a user writes a manual step (without entering a manual XPath) and execution is ON and the step passes, the ‘Relative XPath’ will automatically appear as the default locator and ‘Automator XPath’ will appear as a secondary locator.
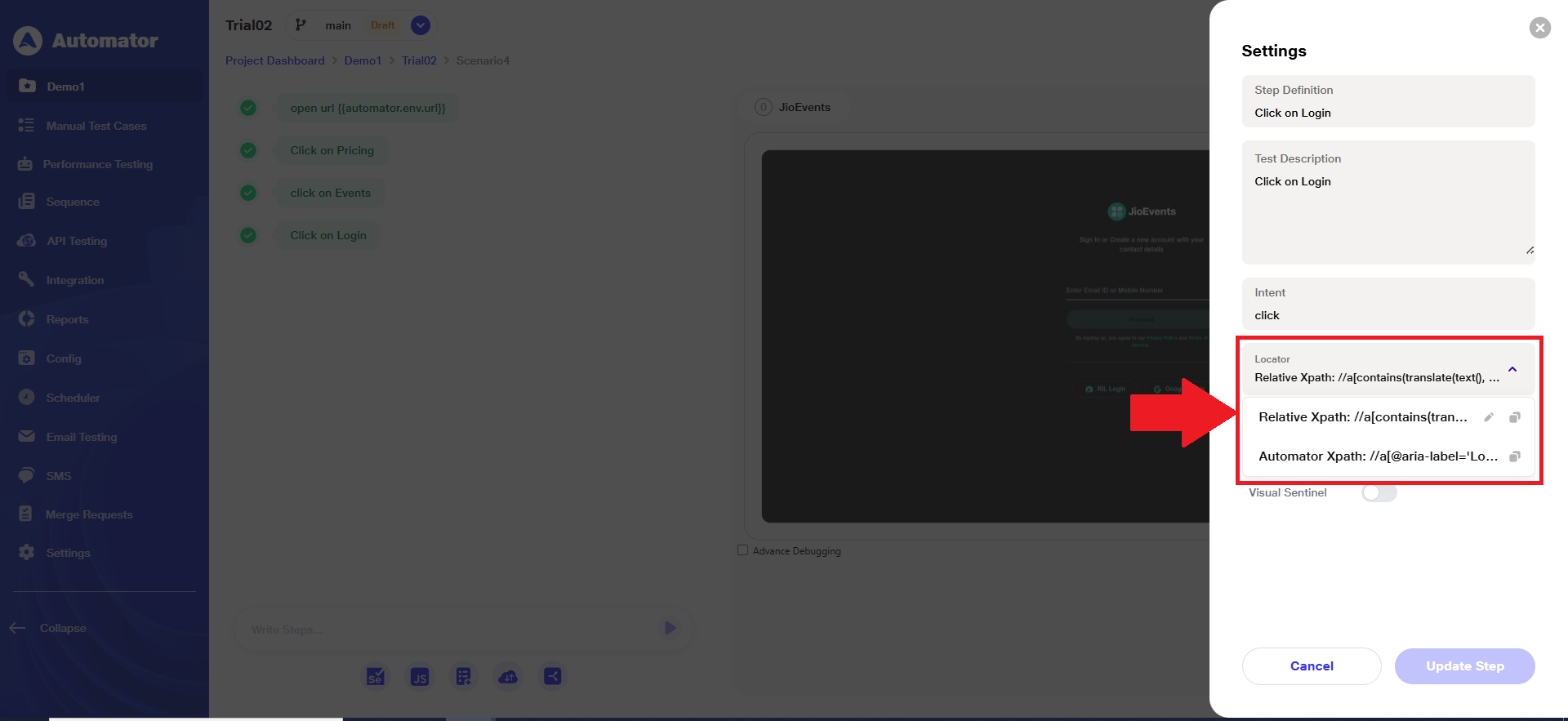 c) When a user writes a manual step (by entering a custom XPath) and execution is ON and the step passes, the manually written XPath (Relative XPath) will become the default locator, while the ‘Automator XPath’ will appear as a secondary locator.
c) When a user writes a manual step (by entering a custom XPath) and execution is ON and the step passes, the manually written XPath (Relative XPath) will become the default locator, while the ‘Automator XPath’ will appear as a secondary locator.
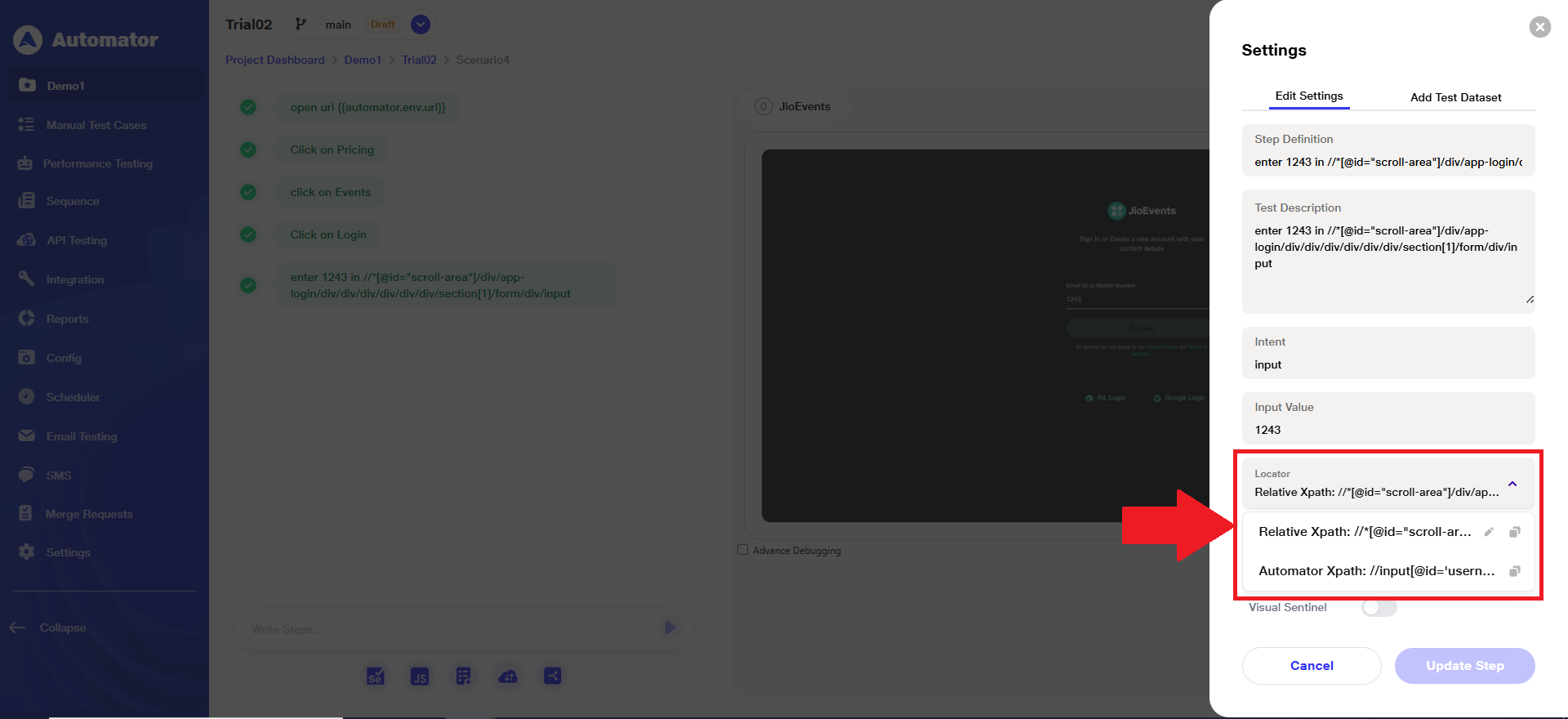 Note: The selected locator can be changed/ edited later, except for the ‘Automator XPath’, which remains non-editable.
Note: The selected locator can be changed/ edited later, except for the ‘Automator XPath’, which remains non-editable.
Step 3: Visual Testing Steps
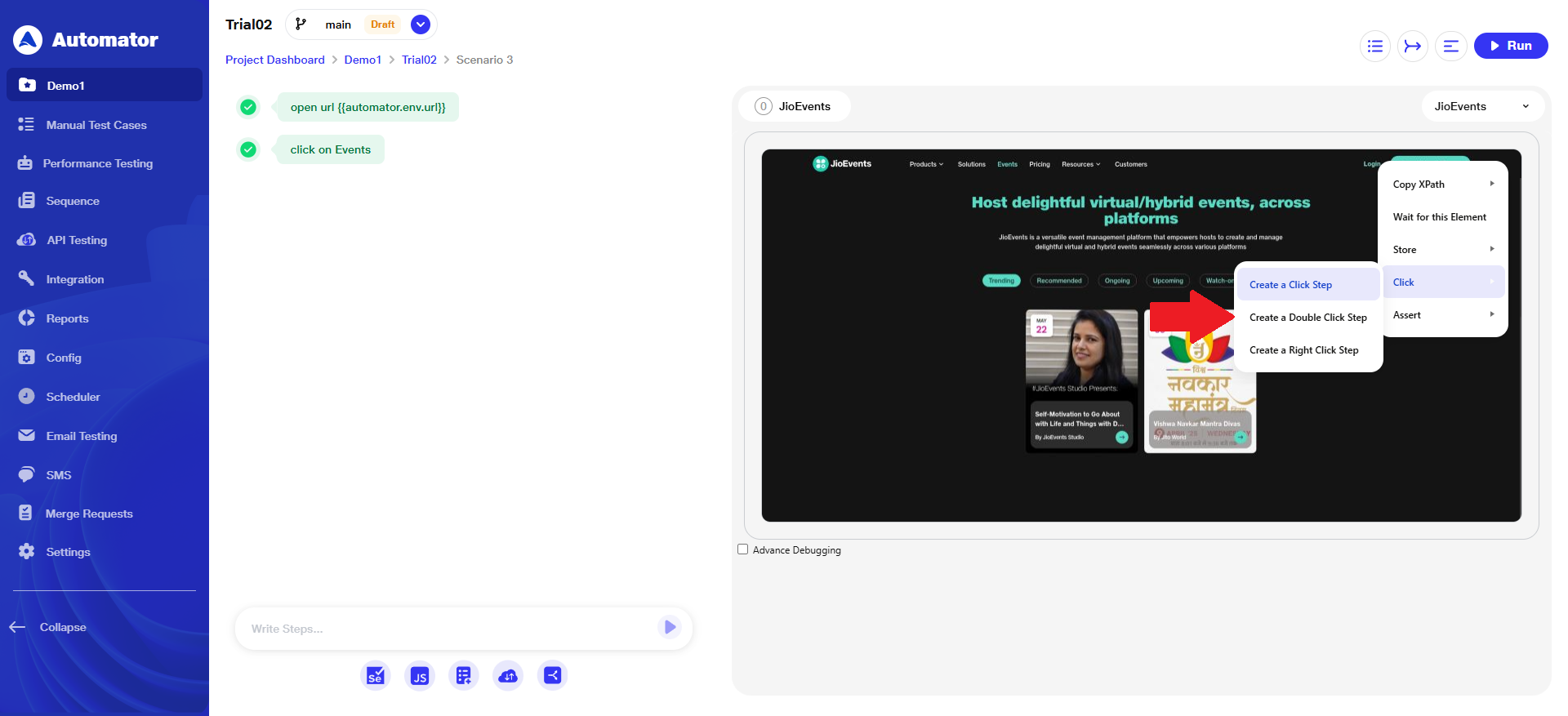
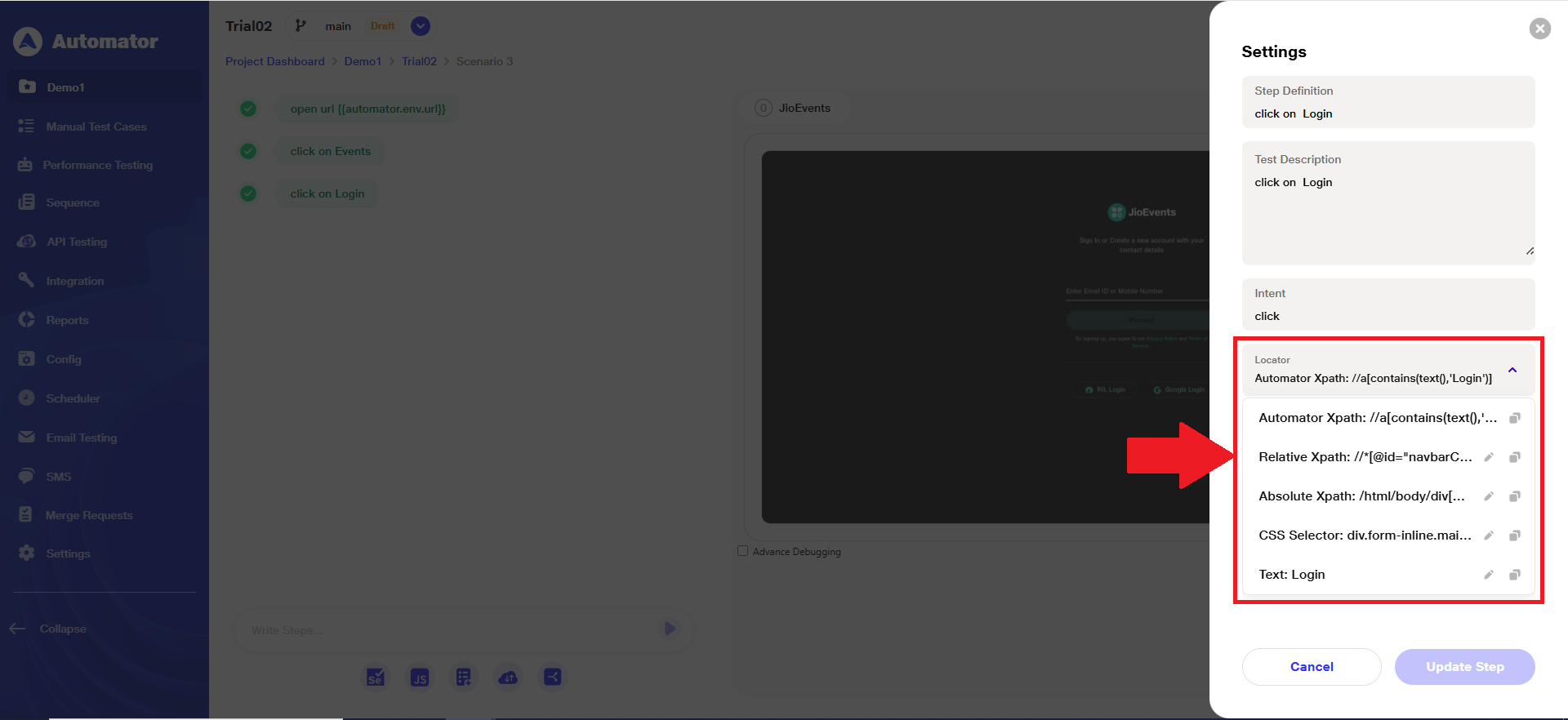
a) On the Visual Testing page, when the user selects Click → Create a Click Step, the non-editable ‘Automator XPath’ will appear as the default locator, and additional editable locators will be visible in the list for selection.
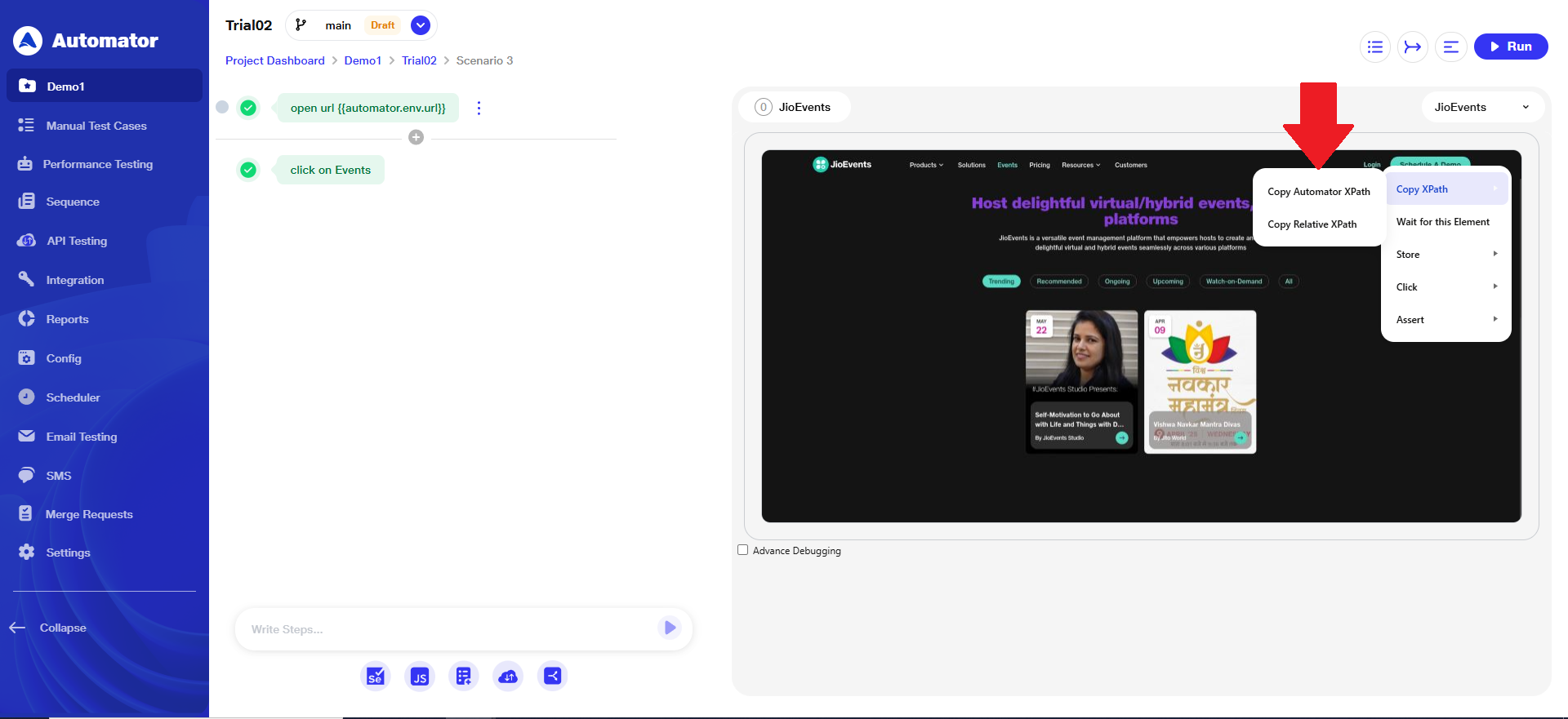
Step 4: Copy XPath Options
a) When copying an XPath, the user will now see two available options:
i) Automator XPath – Optimized version of the Relative XPath.
ii)Relative XPath – Standard relative XPath option.
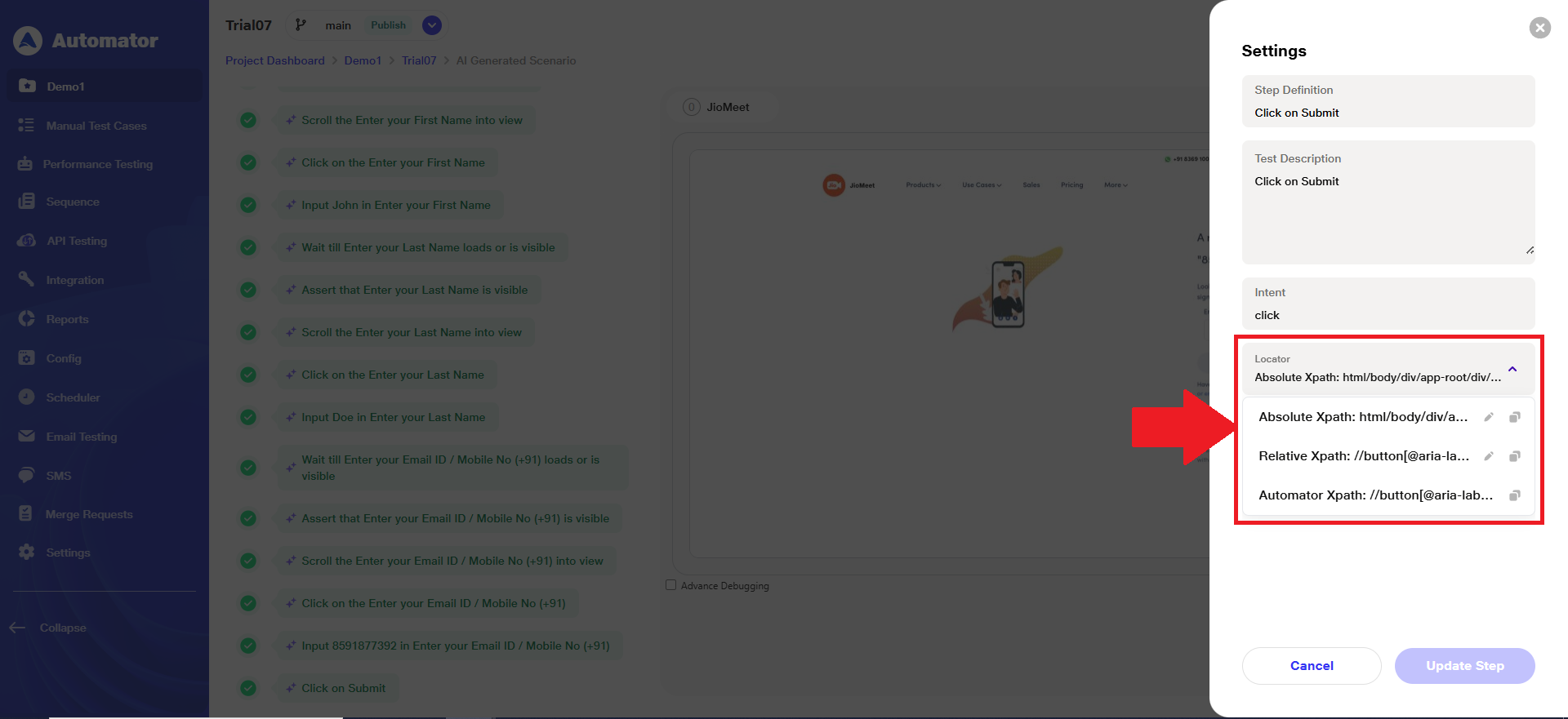
Step 5: AI-Powered Test Cases
a) For AI-generated test cases, when visual testing is ON and a step passes, the ‘Absolute XPath’ automatically becomes the default locator, and all other existing production locators appear in the locator list.
Benefits
1) Automated Locator Creation: Eliminates the need for manual XPath authoring by automatically generating stable, unique, and minimal XPath expressions for web elements.
2) Improved Test Stability: Ensures test reliability by using optimized locators that adapt better to UI changes, reducing script breakages.
3) Reduced Maintenance Efforts: Automatically updates locator behavior, minimizing manual intervention and maintenance effort.
4) Consistent Behavior Across Scenarios: Maintains uniform locator handling for existing, new, manual, and AI-generated steps, ensuring predictable execution outcomes.
5) Enhanced Visual Testing Support: Automatically applies optimized locators during visual testing steps for accurate element mapping and validation.
6) Simplified Locator Management: Introduces ‘Automator XPath’ as the default locator with additional fallback Chrome locators for improved flexibility.
7) Protected Accuracy: Keeps ‘Automator XPath’ non-editable to preserve consistency, prevent human error, and ensure locator reliability across runs.
8) Improved Efficiency: Speeds up test execution setup by auto-assigning the most efficient XPath, helping teams focus on testing rather than locator maintenance.